How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced techniques and safety regulations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will explore the intricacies of drone components, emphasizing the importance of understanding each part’s function for optimal performance and safety. We’ll then delve into the practical aspects of flight, including takeoff, landing, and maneuvering, providing clear instructions and helpful tips to ensure smooth and controlled flights. Finally, we’ll cover essential safety regulations and best practices to guarantee responsible and legal drone operation.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone and their respective functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key parts of a typical drone, their roles, and variations.
Drone Propellers and Their Impact on Flight
Propellers are the rotating blades that generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and land. Different propeller designs influence flight characteristics. Larger propellers generally produce more thrust but may reduce speed, while smaller propellers offer greater speed but less lift. Propeller pitch (the angle of the blade) also affects performance; a higher pitch results in more thrust at lower RPMs, suitable for heavier payloads or windy conditions, whereas a lower pitch offers higher speed but less lift.
Drone Motors and Their Role in Propulsion
Brushless DC motors are the standard for most drones due to their efficiency, power, and relatively low maintenance. These motors convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, spinning the propellers. The motor’s KV rating (RPM per volt) indicates its speed potential, influencing the drone’s overall performance and responsiveness. Higher KV motors offer greater speed but may require more current.
Flight Controllers: The Drone’s Brain
The flight controller is the central processing unit (CPU) of the drone, managing all aspects of flight. It receives input from various sensors (accelerometer, gyroscope, barometer, GPS), processes this data, and sends signals to the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. Different flight controllers offer varying features, such as advanced flight modes (GPS, waypoint navigation), and differing levels of processing power and responsiveness.
For instance, a basic flight controller might only offer basic stability control and manual flight modes, while a more advanced controller could support autonomous flight, obstacle avoidance, and sophisticated camera control. The choice of flight controller often depends on the drone’s intended use and complexity.
Drone Batteries: Powering the Flight
The drone battery is the power source for all onboard components. Battery specifications are crucial for determining flight time and performance. Key specifications include capacity (measured in mAh – milliampere-hours), voltage (typically 3S or 4S LiPo batteries), and C-rating (discharge rate). Higher capacity batteries provide longer flight times, while a higher C-rating allows for greater current draw, beneficial for more powerful motors and demanding flight maneuvers.
| Battery Model | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (S) | Flight Time (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Battery A | 1500 | 3S | 20-25 minutes |
| Example Battery B | 2200 | 4S | 30-35 minutes |
| Example Battery C | 3000 | 6S | 40-45 minutes |
| Example Battery D | 1300 | 3S | 15-20 minutes |
GPS Module: Navigation and Positioning, How to operate a drone
The GPS module allows the drone to determine its location, altitude, and speed relative to the Earth. This data is essential for autonomous flight modes, return-to-home (RTH) functionality, and precise positioning. The accuracy of the GPS signal can be affected by environmental factors such as satellite visibility and atmospheric interference.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers pre-flight checks and maneuvering techniques. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation, allowing you to capture stunning aerial footage responsibly.
Drone Camera: Capturing Aerial Perspectives
The drone camera is responsible for capturing high-resolution photos and videos from the air. Key camera settings include resolution (measured in megapixels for photos and frames per second for video), frame rate, and ISO (sensitivity to light). Understanding these settings is crucial for optimizing image quality and capturing smooth, stable footage.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and reliable drone operation. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents or equipment damage. This section Artikels the necessary checks and procedures.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
Before each flight, a comprehensive inspection is crucial. This should include verifying battery charge, propeller integrity, sensor functionality, and overall structural soundness of the drone. A visual inspection for any damage is also necessary. Ensure all components are securely fastened. Properly calibrated sensors and compass are also important for safe and stable flight.
- Check battery charge level.
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU.
- Check for any physical damage to the drone.
- Ensure all components are securely attached.
- Review flight plan and weather conditions.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensors is critical for accurate flight. The compass ensures correct heading information, while the IMU provides data on the drone’s orientation and movement. Improper calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior or loss of control. Most drones have built-in calibration procedures within their control software.
Safe Drone Operation in Various Weather Conditions
Weather conditions significantly impact drone flight. Wind can affect stability and control, while rain or snow can damage electronic components. It’s crucial to avoid flying in high winds, heavy rain, or snow. Understanding local weather forecasts is essential for safe operation.
Pre-Flight Sequence Flowchart
A structured pre-flight sequence minimizes the risk of errors and ensures a smooth flight. The steps involved typically include powering on the drone and controller, checking battery levels, calibrating sensors, and confirming GPS signal acquisition before initiating takeoff.
A flowchart illustrating this sequence would show a series of steps, starting with powering on the drone and controller, then checking battery level and signal strength, followed by sensor calibration, and finally proceeding to takeoff only after all checks are satisfactory. Any failure at any step would trigger a review of that specific step before proceeding.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are essential for preventing accidents and damage. This section details the proper techniques and precautions.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
A smooth takeoff involves gently increasing throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a steady ascent, avoiding sudden movements. Landing should be performed similarly, gradually decreasing throttle until the drone gently touches down. Avoid abrupt landings, as this can damage the drone or its components.
Altitude Control and Stable Flight
Maintaining stable altitude and flight during takeoff and landing requires precise control of the throttle. Use small, incremental adjustments to avoid jerky movements. Pay close attention to the drone’s response to your inputs, adjusting accordingly to maintain a smooth, controlled flight.
Hazards During Takeoff and Landing and Mitigation
Potential hazards during takeoff and landing include obstacles, wind gusts, and uneven terrain. Careful pre-flight planning and site selection are crucial for mitigating these risks. Maintaining awareness of surroundings and avoiding rushed maneuvers is also essential.
Common Takeoff and Landing Errors and Solutions
- Error: Abrupt takeoff or landing. Solution: Use smooth, incremental throttle adjustments.
- Error: Drifting during takeoff or landing. Solution: Adjust control inputs to compensate for wind or other factors.
- Error: Collision with an obstacle. Solution: Improve situational awareness and pre-flight planning.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to safe and effective drone operation. This section explains the functions of the control sticks and how to perform essential maneuvers.
Functions of Control Sticks
Most drones utilize two control sticks: one for throttle and pitch/roll, and another for yaw. The throttle stick controls altitude (up/down), while the pitch controls forward/backward movement and the roll controls left/right movement. The yaw stick controls rotation around the drone’s vertical axis.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
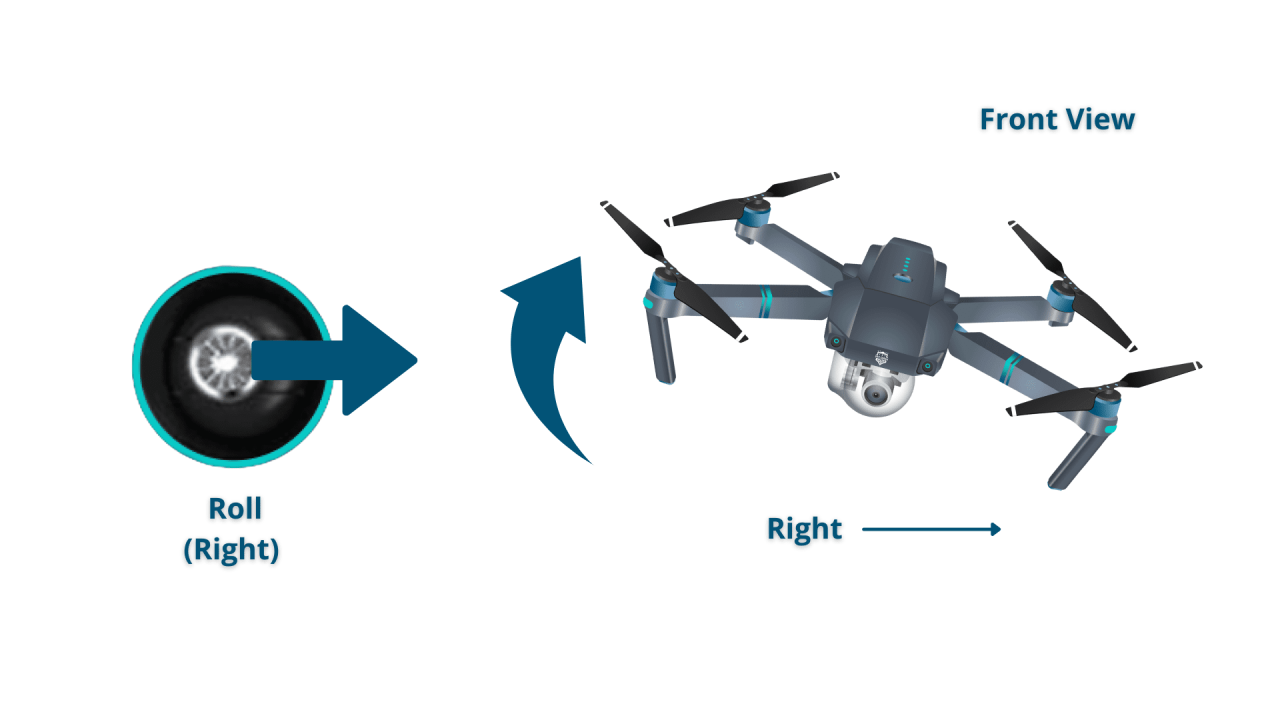
Basic maneuvers include hovering (maintaining a stationary position in the air), ascending (increasing altitude), descending (decreasing altitude), and turning (rotating the drone around its vertical axis). These maneuvers require precise control of the sticks, with small, smooth movements for accurate control.
Maintaining Smooth and Controlled Movements
Smooth and controlled movements are crucial for safe and efficient flight. Avoid jerky or abrupt inputs, using gentle, incremental adjustments to the control sticks. Practice in a safe, open area to develop your control skills.
Relationship Between Control Stick Movements and Drone Response

A visual representation would show a schematic of the control sticks. Moving the left stick upwards increases throttle (ascending), downwards decreases throttle (descending). Tilting the left stick forward moves the drone forward, backward when tilted back, left when tilted left, and right when tilted right. The right stick controls the yaw (rotation) of the drone; right stick to the right rotates the drone clockwise, and to the left rotates the drone counter-clockwise.
Advanced Flight Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
Advanced flight techniques expand the capabilities of drone operation, enabling more complex maneuvers and autonomous flight. However, these techniques require greater skill and awareness of potential risks.
GPS and Autonomous Flight Modes
GPS enables autonomous flight modes, such as return-to-home (RTH), waypoint navigation, and follow-me. These modes require a strong GPS signal and careful planning to ensure safe operation.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available online; for a comprehensive guide, check out this helpful article on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation.
Flying in Challenging Environments
Flying in windy conditions requires greater control and skill. Adjusting control inputs to compensate for wind gusts is crucial for maintaining stability. Flying in confined spaces demands precise control and awareness of surrounding obstacles.
Comparison of Flight Modes
Manual mode provides direct control over the drone’s movements. GPS mode utilizes GPS data for stabilization and autonomous functions. Waypoint mode allows for pre-programmed flight paths. Each mode has its advantages and disadvantages depending on the situation and pilot skill level.
Potential Risks of Advanced Flight Maneuvers and Mitigation
Advanced maneuvers increase the risk of accidents. Careful planning, proper training, and awareness of limitations are crucial for mitigating these risks. Always prioritize safety and avoid pushing the limits of your skills or the drone’s capabilities.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Optimizing drone camera settings is essential for capturing high-quality photos and videos. This section details the key settings and techniques for achieving optimal results.
Drone Camera Settings

Understanding camera settings such as resolution, frame rate, and ISO is crucial for achieving the desired image quality. Higher resolution provides greater detail, while a higher frame rate results in smoother video. ISO affects the image’s sensitivity to light, influencing brightness and noise levels.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Capturing high-quality images requires careful consideration of lighting, composition, and camera settings. Experiment with different settings to find the optimal balance between resolution, frame rate, and ISO for various lighting conditions.
Optimal Image Stabilization
Achieving optimal image stabilization is crucial for smooth, professional-looking footage. Many drones offer electronic image stabilization (EIS), which helps compensate for camera shake. Flying smoothly and avoiding jerky movements also contributes to stable footage.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Different Lighting Conditions
Lighting conditions significantly affect image quality. Adjusting ISO and other settings is necessary to optimize image exposure and minimize noise in various lighting scenarios. For low-light conditions, a higher ISO might be necessary, while bright conditions may require a lower ISO to avoid overexposure.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued reliable performance. This section Artikels the necessary procedures.
Routine Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include inspections for physical damage, cleaning of the drone and its components, and lubrication of moving parts. The frequency of maintenance depends on usage but should be performed at least after every few flights.
Cleaning and Storage Procedures
Clean the drone and its components regularly using a soft cloth and appropriate cleaning solutions. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Store the drone in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Identifying and Addressing Common Drone Malfunctions
Common malfunctions include battery issues, motor problems, and sensor errors. Understanding these potential issues and troubleshooting techniques is crucial for maintaining drone functionality.
Essential Maintenance Tools and Supplies
- Soft cloths
- Isopropyl alcohol
- Screwdrivers
- Propeller balancer
- Battery charger
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. This section highlights key considerations and provides a checklist for compliance.
Relevant Laws and Regulations (User to Specify Location)
Drone regulations vary by location. Before flying, it is crucial to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area. This includes obtaining any necessary permits or licenses, registering your drone, and adhering to airspace restrictions.
For example, in many jurisdictions, flying near airports or other restricted airspace is prohibited. Operating within a certain distance from people or structures is also regulated to ensure public safety.
Safe Operating Distances
Maintaining safe operating distances from people, buildings, and other aircraft is crucial for preventing accidents and damage. Always be aware of your surroundings and avoid flying too close to anything that could pose a hazard.
Respecting Privacy and Avoiding Unauthorized Airspace
Respecting privacy and avoiding unauthorized airspace is essential for responsible drone operation. Do not fly over private property without permission and avoid recording individuals without their consent. Familiarize yourself with local airspace restrictions and adhere to them strictly.
Safety Regulations Compliance Checklist
- Check local drone regulations.
- Register your drone (if required).
- Obtain necessary permits (if required).
- Maintain safe operating distances.
- Respect privacy and avoid unauthorized airspace.
- Fly only in safe and legal areas.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with a responsible approach. By understanding the mechanics of flight, adhering to safety regulations, and continuously practicing, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember, safe and responsible operation is paramount, ensuring both your safety and the safety of others. This guide serves as a foundation; continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and confident drone pilot.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the maximum flight time for most consumer drones?
Flight times vary significantly depending on the drone model and battery size, typically ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency stop function if available. If unsuccessful, try to land the drone in a safe, open area away from people and property. Report the incident to the relevant authorities.
What is the best way to clean my drone?
Use a soft, damp cloth to gently wipe away dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Consult your drone’s manual for specific cleaning instructions.
